Artificial Insemination
What is Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)?
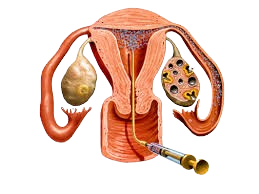
Intrauterine insemination (IUI), also known as artificial insemination, involves the direct placement of specially washed sperm into a woman’s uterus during her fertile window, close to ovulation. The desired outcome of IUI is for the sperm to travel through the fallopian tubes and fertilize an egg, resulting in natural pregnancy.
Infertility is a complex condition, with some causes linked to hormonal imbalances, a woman’s age, issues with the cervix or ovaries, or male infertility factors such as low sperm count or poor sperm quality. Addressing infertility often requires consulting an experienced specialist to assess and treat the condition, as IUI may be suitable for certain cases, while others may need different approaches.
Why is Intrauterine Insemination Performed?
IUI is generally used to overcome issues such as low sperm count or poor sperm motility. If semen analysis shows a sperm concentration lower than average, weak motility, or abnormalities in size or shape, a doctor may recommend IUI. This method can help improve the chances of fertilization by washing the sperm with special solutions to separate the healthier, more active sperm from those of lower quality.
IUI can also address cervical problems. By placing sperm directly into the uterus, it bypasses issues like severe vaginal sensitivity to proteins in semen (which is rare), thick cervical mucus, or scarring in the cervix or vagina due to prior surgeries. IUI increases the number of sperm available for fertilization.
IUI may be an option for other infertility causes, such as:
- Unexplained infertility: When the cause of infertility cannot be identified, IUI may be combined with ovulation-stimulating medications.
- Endometriosis-related infertility: For women with endometriosis, using medications to improve egg quality along with IUI can often be beneficial.
Steps of Intrauterine Insemination
Men Intrauterine Insemination
IUI involves several steps. For men, the semen sample is processed and washed to remove proteins that may cause allergies and to improve sperm quality and count. The sperm is then separated into high-quality, active sperm and lower-quality sperm.
Women Intrauterine Insemination
For women, preparation starts with monitoring ovulation. Timing is crucial for IUI success, so while at-home ovulation tracking is possible, doctors typically use ultrasound to monitor ovarian follicles and the growth of eggs, sometimes prescribing medications to stimulate ovulation.
Time
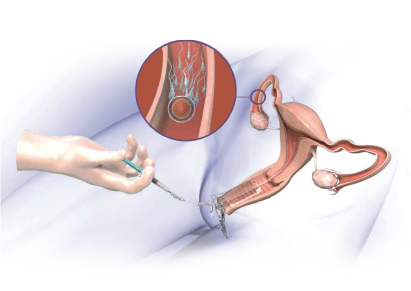
The IUI procedure itself is quick, typically taking 15 to 20 minutes. It does not require anesthesia. A thin tube is inserted into the uterus via the cervix, and the prepared sperm is injected into the uterine cavity. After the procedure, the woman is asked to lie down for a short period before resuming her usual activities.
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ
What Are the Main Risks of Intrauterine Insemination?
IUI is a relatively simple and safe procedure, but, in rare cases, complications may occur, including:
Infection: This risk exists with all medical procedures, even simple ones, but proper sterilization techniques and following the doctor’s guidelines can greatly reduce this risk.
Mild vaginal bleeding: The insertion of the catheter into the uterus may cause slight irritation, leading to a small amount of bleeding, which usually does not affect pregnancy chances.
Multiple pregnancies: While IUI itself is not directly linked to an increased risk of multiple pregnancies (twins or more), the use of ovulation-stimulating medications along with IUI significantly raises the likelihood of multiple pregnancies.
When Can Pregnancy Tests Be Done?
Pregnancy tests should be performed about two weeks after the procedure. Testing too early can lead to inaccurate results. For instance, a negative result may occur even if fertilization has happened because pregnancy hormones may not yet be detectable. On the other hand, if the woman was given ovulation-stimulating drugs such as HCG, the medication’s lingering effects could give a false positive result.
Blood pregnancy tests are preferred over urine tests, as they are more sensitive and accurate.
What is the Success Rate?
The success rate of IUI varies depending on multiple factors, such as the woman’s age, the cause of infertility, the use of fertility medications, and the experience of the treating physician. IUI requires careful preparation, and every step in the procedure affects its success. Therefore, selecting a reputable doctor with experience and a well-equipped clinic with advanced technologies is essential to maximize the chances of success.