Ovarian Cystectomy
What is an Ovarian Cyst?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs located within or on the surface of the ovary. These are common occurrences among women and are usually benign. While most ovarian cysts resolve on their own and cause no symptoms, they can occasionally lead to complications, such as reduced fertility. In such cases, a physician may recommend aspirating the cyst to remove the fluid.
When is Ovarian Cyst Aspiration Necessary?
Ovarian cyst aspiration becomes essential if the cyst causes symptoms such as:
- Irregular menstrual cycles.
- Pelvic pain or cramps.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Pain during intercourse.
Fertility issues.
Other factors influencing the decision to aspirate include the size and appearance of the cyst and the patient’s age, especially for women post-menopause.
How is Ovarian Cyst Aspiration Performed?
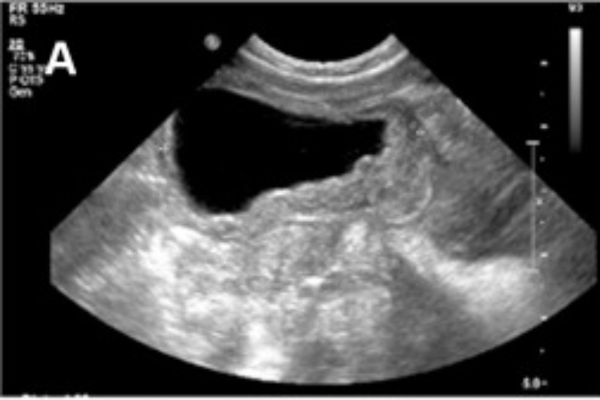
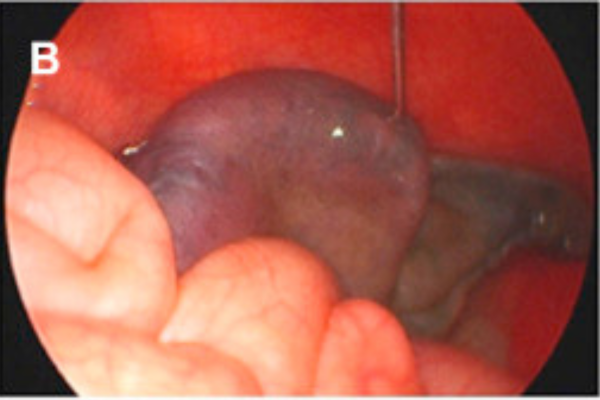
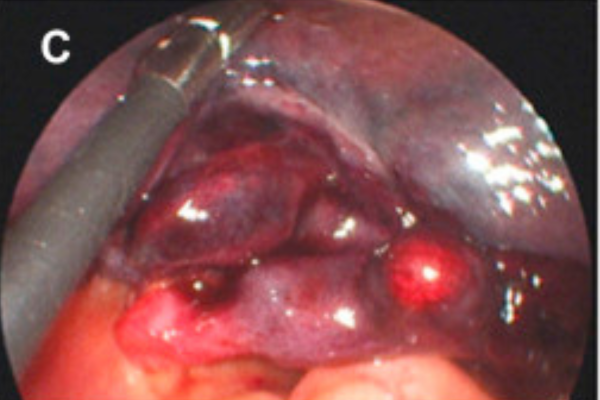
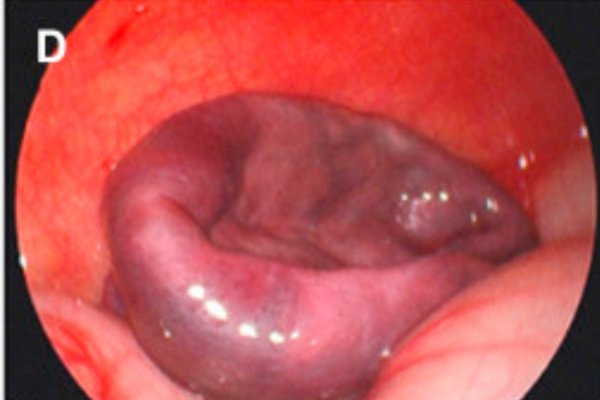
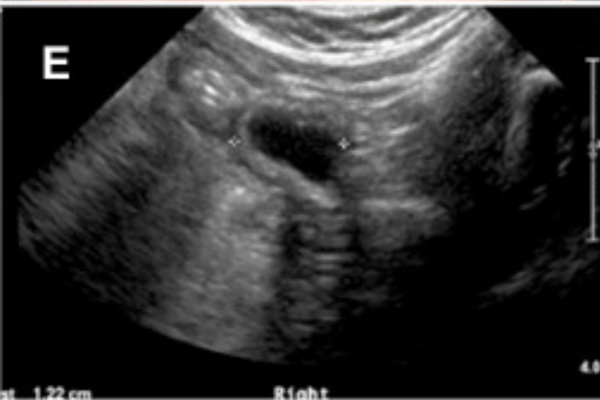
Ovarian cyst aspiration involves using a laparoscope or ultrasound to assess the nature of the ovarian cysts. Determining the type of cyst and the nature of the fluid inside is critical before the procedure. After the assessment, a small needle is inserted into the cyst, and the fluid is aspirated after the patient is anesthetized.
The procedure typically takes about 20 minutes, but the total time is longer, as it includes preparation and anesthesia, and the patient needs time to fully recover from the anesthesia. Afterward, the fluid sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis to ensure the cysts are safe.
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ
What is Ovarian Cyst Aspiration?
Ovarian cyst aspiration is a simple and safe procedure used to drain the fluid from an ovarian cyst without the need for extensive surgery or the removal of the entire ovary or part of it. This procedure is typically successful; in most cases, draining the fluid from the cyst is sufficient, and no further medical intervention is required.
Who Should Undergo Ovarian Cyst Aspiration?
If ovarian cysts are detected during a routine examination, your doctor may recommend monitoring the cysts, as many of them will resolve on their own without any medical or surgical intervention, particularly if they are asymptomatic. However, if the ovarian cysts are accompanied by symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles, abdominal cramps and pain, heavy bleeding, pain during intercourse, or infertility, it may be time to consider aspirating the cysts and draining the fluid.
In addition to the presence of symptoms, several factors play a role in deciding whether to proceed with cyst aspiration, such as:
The size and shape of the ovarian cyst.
The woman’s age: Cysts found in women who have gone through menopause are usually removed.
What to Expect After Ovarian Cyst Aspiration?
The patient will need several days of rest, during which she should avoid strenuous activities, lifting heavy objects, and follow all the doctor’s recommendations to prevent complications. Compared to surgery, cyst aspiration is much easier, less painful, and recovery is quicker.
Side effects of ovarian cyst aspiration are rare, but mild cramping or abdominal pain may occur, which usually responds to regular pain relievers. Light bleeding may also occur, and infection is a possibility. There is also a chance that the cyst may recur, so the ovaries should be monitored with ultrasound.
What is the Effect of Ovarian Cyst Aspiration on Patients Undergoing In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)?
Ovarian cysts can lead to reduced fertility, making it important to drain these cysts in women struggling to conceive, particularly if the cyst is large. For smaller cysts, your doctor may advise ignoring them.
However, draining these cysts becomes even more critical during in vitro fertilization (IVF). Large cysts can negatively impact the success of IVF, so it is preferable to remove them, especially if IVF has failed repeatedly. When IVF fails, your doctor will likely recommend rest and cessation of attempts for a month or more to allow the ovaries to recover and for the cysts to be drained before trying again.